Getting Started
Paste these commands into your favorite terminal on Windows, Mac, or Linux. This will install the Terminal.Gui.Templates, create a new "Hello World" TUI app, and run it.
(Press Esc to exit the app)
dotnet new install Terminal.Gui.Templates@2.0.0-beta.*
dotnet new tui-simple -n myproj
cd myproj
dotnet run
Adding Terminal.Gui to a Project
To install Terminal.Gui from Nuget into a .NET Core project, use the dotnet CLI tool with this command.
dotnet add package Terminal.Gui
Using the Templates
Use the Terminal.Gui.Templates:
dotnet new install Terminal.Gui.Templates@2.0.0-beta.*
Sample Usage in C#
The following example shows a basic Terminal.Gui application using the modern instance-based model (this is ./Example/Example.cs):
// A simple Terminal.Gui example in C# - using C# 9.0 Top-level statements
// This is a simple example application. For the full range of functionality
// see the UICatalog project
using Terminal.Gui.App;
using Terminal.Gui.Configuration;
using Terminal.Gui.ViewBase;
using Terminal.Gui.Views;
// Override the default configuration for the application to use the Amber Phosphor theme
ConfigurationManager.RuntimeConfig = """{ "Theme": "Amber Phosphor" }""";
ConfigurationManager.Enable (ConfigLocations.All);
IApplication app = Application.Create ().Init ();
var userName = app.Run<ExampleWindow> ().GetResult<string> ();
app.Dispose ();
// To see this output on the screen it must be done after Dispose,
// which restores the previous screen.
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty (userName))
{
Console.WriteLine (@"Login cancelled");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine ($@"Username: {userName}");
}
// Defines a top-level window with border and title
public sealed class ExampleWindow : Runnable<string?>
{
public ExampleWindow ()
{
Title = $"Example App ({Application.QuitKey} to quit)";
// Create input components and labels
var usernameLabel = new Label { Text = "Username:" };
var userNameText = new TextField
{
// Position text field adjacent to the label
X = Pos.Right (usernameLabel) + 1,
// Fill remaining horizontal space
Width = Dim.Fill ()
};
var passwordLabel = new Label { Text = "Password:", X = Pos.Left (usernameLabel), Y = Pos.Bottom (usernameLabel) + 1 };
var passwordText = new TextField
{
Secret = true,
// align with the text box above
X = Pos.Left (userNameText),
Y = Pos.Top (passwordLabel),
Width = Dim.Fill ()
};
// Create login button
var btnLogin = new Button
{
Text = "Login",
Y = Pos.Bottom (passwordLabel) + 1,
// center the login button horizontally
X = Pos.Center (),
IsDefault = true
};
// When login button is clicked display a message popup
btnLogin.Accepting += (s, e) =>
{
if (userNameText.Text == "admin" && passwordText.Text == "password")
{
MessageBox.Query (App!, "Logging In", "Login Successful", "Ok");
Result = userNameText.Text;
App!.RequestStop ();
}
else
{
MessageBox.ErrorQuery ((s as View)?.App!, "Logging In", "Incorrect username or password", "Ok");
}
// When Accepting is handled, set e.Handled to true to prevent further processing.
e.Handled = true;
};
// Add the views to the Window
Add (usernameLabel, userNameText, passwordLabel, passwordText, btnLogin);
}
}
Key aspects of the modern model:
- Use Application.Create() to create an IApplication instance
- The application initializes automatically when you call
Run<T>() - Use
app.Run<ExampleWindow>()to run a window that implements IRunnable - Call
app.Dispose()to clean up resources and restore the terminal - Event handling uses Accepting event instead of legacy
Acceptevent - Set
e.Handled = truein event handlers to prevent further processing
When run the application looks as follows:
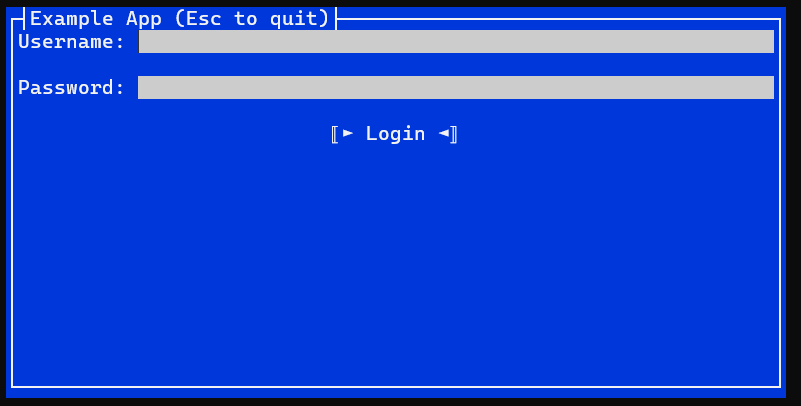
Building the Library and Running the Examples
- Windows, Mac, and Linux - Build and run using the .NET SDK command line tools (
dotnet buildin the root directory). RunUICatalogwithdotnet run --project UICatalog. - Windows - Open
Terminal.slnwith Visual Studio 202x.